In the current digital business environment, search engines have become the most critical link in the decision-making chain. Whether searching for professional technical solutions or evaluating global supply chain partners, decision-makers often start with the Google search box. However, many businesses face the dilemma of “clicks without conversions” or “high advertising costs” when investing in Google Search Ads. To break through these bottlenecks, simply increasing the budget is not the cure; a deep understanding of the underlying operational logic and algorithmic rules is the only path to achieving a high Return on Investment (ROI).
Table of Contents
I. The Underlying Logic of Google Search Ads: Auction Mechanism and Value Exchange
The core of Google Search Ads is not a traditional “highest bidder wins” system, but a complex real-time auction system. Google’s business model is built on providing users with “the most relevant and valuable” information. Therefore, its algorithm aims to balance the interests of three parties: users get accurate answers, advertisers get precise traffic, and Google receives reasonable advertising revenue.
When a user enters a specific command or phrase, the system triggers an auction within milliseconds. This auction determines two key dimensions of the ad: Ad Rank and Actual Cost Per Click (Actual CPC). Understanding this is crucial for optimizing corporate promotions because, in professional markets with long decision cycles and high order values, every click represents a potential business opportunity.
80%of users ignore paid ads and focus on high-quality information content
63%of clicks come from the top three ad positions
10/10A perfect Quality Score can reduce CPC by up to 50%
3.75%is the average CTR for Google Ads across all industries
II. The Trinity of Ranking: Bidding, Quality Score, and Ad Rank
The key formula determining whether an ad appears before potential customers is: Ad Rank = Bid × Quality Score + Expected Impact of Ad Assets. This means that even with a limited budget, you can still outrank competitors with deeper pockets by significantly improving ad quality.

1. Bidding Strategy
A bid represents the maximum amount an advertiser is willing to pay for a single click. In decision-oriented business scenarios, manual bidding is gradually being replaced by AI-driven Smart Bidding. According to official Google documentation, Smart Bidding uses machine learning to dynamically adjust for geographic location, device, time, and user intent during each auction.
2. Core Components of Quality Score
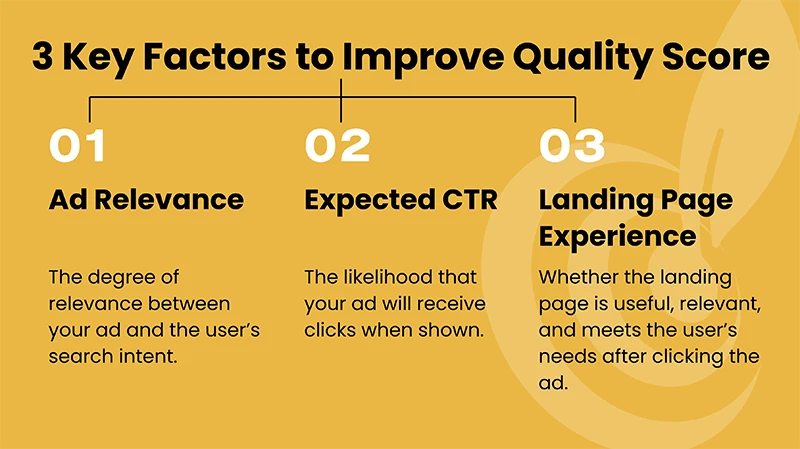
Quality Score is Google’s 1-to-10 evaluation of overall ad quality. It is determined by three dimensions:
- Expected Click-Through Rate (Expected CTR): The system’s prediction of the likelihood the ad will be clicked. This reflects how well the ad headline matches the user’s search intent.
- Ad Relevance: The degree of correlation between keywords and ad copy.
- Landing Page Experience: The experience after a user clicks. This includes page load speed, whether the content solves the user’s problem, and mobile-friendliness.
3. Ad Assets
Including sitelinks, call info, structured snippets, etc. These elements not only increase the ad’s footprint but also provide additional decision-making information, significantly boosting CTR.
III. How to Operate with Precision? From Keyword Filtering to Copywriting
When promoting professional services or high-value products, precision is far more important than total traffic volume. Here are the core operational steps:
Keyword Research and Intent Classification
We must distinguish between “Informational” and “Transactional” search intents. For example, someone searching for “what is enterprise cloud service” might still be in the research phase, while someone searching for “enterprise cloud service quotation” has strong purchase intent. In the practical experience of HeyaDigi Digital Advertising, we suggest clients design differentiated landing pages for different keyword stages.
| Keyword Type | User Intent | Suggested Strategy | Expected Conversion Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brand Terms | Loyal customers or existing awareness | Protect brand traffic, high bids | Very High |
| Product/Service Terms | Seeking specific solutions | Emphasize core advantages and differentiation | Medium to High |
| Industry Long-tail Terms | Specific pain point resolution | Provide in-depth technical articles or whitepapers | Medium |
| Competitor Terms | Comparison stage | Emphasize Unique Selling Proposition (USP) | Low to Medium |
Copywriting Psychology: Building Trust and Authority
Copy in professional fields should not overemphasize “cheapness” but focus on “professionalism, stability, and success stories.” Using specific data (e.g., assisted over 500 companies in transformation) is more persuasive than empty adjectives. Additionally, ensure keywords are included in the copy, which is vital for improving “Ad Relevance.”
Case Study: Transformation of an Industrial Automation Component Supplier
Challenge: The supplier’s CPC on Google Ads was rising annually, but the quality of leads was poor, with many inquiries unrelated to core business.
Optimization Plan:
1. Keyword Filtering: Excluded negative keywords like “DIY” and “retail,” targeting long-tail terms like “industrial grade” and “bulk procurement.”
2. Quality Score Improvement: Redesigned landing pages, turning cluttered product pages into “Solution Whitepapers” targeting specific industry pain points. Load speed improved from 5s to 1.8s.
3. Bidding Strategy Adjustment: Shifted from “Maximize Clicks” to “Target CPA (tCPA),” letting the algorithm lock onto high-intent users.
Final Results: Ad Rank improved, average CPC dropped by 32%, and inquiries from valid corporate clients grew by 145%.
IV. Deep Relationship Between Quality Score and Ad Rank: The Secret to Lowering Costs
Many advertisers mistakenly believe that simply “raising the bid” secures a good position. In fact, Google uses a Second-Price Auction mechanism. The amount you actually pay is: (Ad Rank of the next competitor / Your Quality Score) + $0.01.
This means if your Quality Score is 10 and your competitor’s is 5, you only need to pay half of their bid to get a better ranking. This is why “optimizing web experience” and “enhancing ad relevance” are among the highest ROI tasks in digital marketing. At heyadigi.com, we always insist on technical optimization to save unnecessary advertising budget waste for enterprises.
V. Conclusion: Continuous Optimization is the Only Path to Success
Google Search Ads is not a “set it and forget it” system. The market environment, competitor bids, and user search habits are constantly changing. Businesses should establish a weekly review mechanism, analyze Search Terms Reports to identify invalid clicks for negative keywords, and discover new growth points.
For companies seeking long-term growth, viewing Google Search Ads as a data collection tool is equally important. Through the data feedback from ads, you can learn which selling points resonate most with customers, thereby optimizing your overall product strategy. In this data-driven era, only by mastering the underlying logic can you remain invincible in the competitive search dividend landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is my google search ads rank low despite a high bid?
This is because Ad Rank depends not only on the bid but is also heavily influenced by Quality Score. If your ad relevance is low or landing page experience is poor, your ranking may be lower than competitors with excellent Quality Scores, even if you bid higher.
What is the most important factor for Quality Score?
While Google does not explicitly give weights, practical experience shows that “Click-Through Rate (CTR)” is usually the most significant factor because it most directly reflects the fit between the ad and the user’s search intent.
Should businesses use manual or smart bidding?
If your account has enough monthly conversion data (usually 30+ recommended), Smart Bidding (such as tCPA or Target ROAS) can leverage AI for more precise real-time optimization. However, when initial data is insufficient, manual CPC or maximizing clicks may help gather initial data.
How to improve landing page experience?
Ensure webpage content matches ad promises, optimize mobile loading speed, and simplify conversion processes (such as form filling). Providing clear calls to action (CTA) and authoritative information content is also key.